Waste Stabilization pond
Description of the emergency context
Currently, there are 929,606 Rohingya refugees residing in 33 congested camps that have been officially designated by the Government of Bangladesh. This population surge occurred as a result of the extreme violence outbreak in Myanmar's Rakhine State on August 25, 2017, which led to an estimated 687,000 Rohingya refugees crossing the border into Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh. The Rohingya refugees have repeatedly sought refuge in Bangladesh due to ongoing persecution. Previous significant influxes occurred following acts of violence in Rakhine State in 1978, 1992, 2012, and once again in 2016. However, the largest and most rapid refugee influx from Myanmar into Bangladesh began in August 2017.
Operating within highly congested settings, such as the Rohingya camps, WASH actors face numerous challenges in implementing effective faecal sludge treatment processes that can efficiently remove pathogens. These challenges primarily stem from space limitations, which impose constraints on the inclusion of appropriate, safe, and sustainable processes for treatment.
Description of the treatment process
- Description of the treatment process:
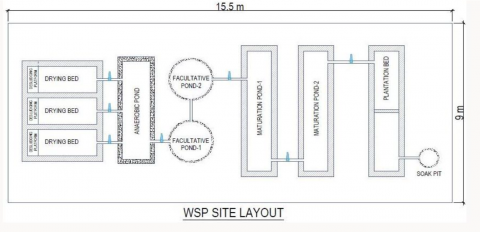
The sludge from latrines is emptied into the transfer points which are connected to the FSTP from different directions using motor pump like mud pump. The primary sludge storage chambers has a capacity is 500 liters. Which points are situated in high elevation for maintain sludge transfer gravity flow.
- Drying Bed:
Solid & liquid parts have separate here. There have Three drying bed which dimension are (3.04m x 1.21m x 1.06m-every bed size). Sludge drying takes 10 to 20 days. Avg. 15 days. Here, both the incoming and dried sludge are pathogenic. Sludge can be composted before reuse to enhance pathogen removal.
- Anaerobic Pond:
This pond main purpose to provide pre-treatment as they remove loads and settled solid without oxygen. Pond dimension (2.74m x 1.21m x 4.57m). Its primary function is BOD removal. This wastewater color normally dark brown to.
- Facultative Ponds:
There have two Facultative Pond. Each Pond size (1.83m Dia x 1.98m Height). The primary function is the removal of BOD. To have clear water, light penetration and photosynthetic of oxygen to decompose organic materials take place easier. The wastewater settles and biodegradable in an anaerobic process. This pond normally influent received. Sometimes the color is bluish to green. Retention time is 1 day/ 24 hrs.
- Maturation Pond:
This pond have two ponds and received the effluent from the facultative pons and their size and number depends on the required bacteriological quality of the final effluent. This pons size same (5.59m x 1.06m x 1.52m). Its also remove BOD but they make significant contribution to nitrogen and phosphorous removal. The main objective of this pond to remove pathogenic microorganisms present in the wastewater which occur mainly due to sun light in the water column.
- Plantation Bed:
This bed has first class stone chips which are different size. There have kolaboty tree which indicate WSP functionality. The stone chips change watercolor & kolaboty tree helps to water evapotranspiration to the earth.
- Polishing Pond:
This pond also known as finishing pond. Receive water flowing from the oxidation pond or from some other secondary treatment system. Here, additional BOD, Solid, feal coliform and some nutrients are removed.
Assessment & design (feasibility)
The total cost for implementing the UNICEF system is USD 12500, which covers all the necessary materials, such as plastic tanks, fittings, filter media, stone chips, PVC pipes, gate valve, geotextile, and fencing. It also includes the construction work, such as site preparation, digging infiltration trenches and sludge pits, and installing hardware materials for the tank. All the materials used in this system are locally sourced and readily available worldwide.
FS characteristics: values where obtained from the WASH cluster
During the site identification stage of the project, it is crucial to find a suitable location considering the challenging and crowded nature of the camps. Several key parameters need to be taken into account during the assessment.
Population: The targeted population should be considered, keeping in mind that each system can serve a maximum of 5,720 users.
Latrine Covarage: 286 doors
Surface area: Approximately 167 m2 of land is required for the totla Treatment.
Soil infiltration rate: Testing and calculation of the soil's infiltration rate is necessary for each site.
Groundwater levels: Here the aviodable.
Flood-prone areas: It is imperative to avoid locating the system in flood-prone areas.
Proximity to water sources: Infiltration trenches should be at least 30 meters away from the nearest water point.
Construction
Pre construction:
- For construction this facilities at first need to check topography level.
- Do need assesment.
- Then do FDG's with beneficaries/communities about this.
-Besides, need to ready design & BOQ then need to submit this WASH sector.
- After, need to site visit with focule person s likes: govt employee/CiC/SMS/SD.
- There have also checked nearest water source distance.
-Maintain to keep good environment.After all kinds of verification need to start work.
During Construction:
- After selection vendor, need to do layout to the field by direction from design.
-All kinds of materilas need to be quality checked.
- Ensure, all construction support materilas likes: mixer machine,vibrator machine,water.
- During the construction maintain curing.
-During construction we ensure sfatety eqipment likes sorrounding area fenching/ marking cution tape and other eqipments.
-All workers maintained safety helmet,gumboat,hand goolves( mask also-during crusial time).
-Ensure all kinds of quality control likes custing & brick working time.
-During construction time, maintain MB book/ daily work record book.
-Ensure proper construction ratio where its needed.
-We ha ve follow govt worker law.
-Don't engage here children workers.
-For daily materilas received & stock maintain ensur a guard for this.
After Construction:
- After construction work we do all work component checked as per design & BOQ.
- We ensure completed work monitoring by our management and doner level authority.
- All work accepted by EIC
- After work we do vendor billing process
Operation and maintenance
Waste Stabilaization Pond Summery:
Parameters tested between inlet and outlet show significant reduction, demonstrating the effectiveness of the treatment mechanism:
COD: 89%
BOD: 92%
TN: 40%
TP: 85%
- Raw sludge quality varies, making it unsuitable for use in congested camps.
- Infiltration process depends on soil characteristics.
Desludging and O&M (refer to SOP):
- Each FSM 1 team for 5 days and each team member is 5.
- FSTP capacity 5m3/day.
- Required materials for Desludging- 1 Mud pump, 1 generator and hose pipe need as per distance from source to FSTP.
- Those materials used where need desludge.
- Used transfer station for collecting sludge which latrines are so far from FSTP.
- Regular monitoring by trained staff is essential for preventive maintenance.
- Ensure worker safety issue during desludging time by serving mask,gum boat,safety googles,helmet.
- Provide cleanness materials, likes- Bathing soap, Laundry soap, ditergent powder and hand senitizer.etc.
- Maintain daily record book.
- Ensure a guard for security.
Lessons learned
1) Public health friendly procedure operated which better than other FSTP.
2) Community provide positive feedback that it's not spreading bad smell
3) Bio chemical Oxyzen dmenad & Chemical Oxyzen demnad result come rapid and correct
Strengths
Relativity low area required.
Operation & Maintenance cost is low.
Easy Operation & Maintenance process.
safe operation.
Environmental friendly.
Required less skill worker.
Environmental friendly technology.
No use of chemicals.
Easy to build, not very skilled labour needed.
Materials locally available.
Environment friendly Effluent.
Weaknesses
Hard to manage FSTP land area.
As hilly area possibility to landslide.

Add new comment