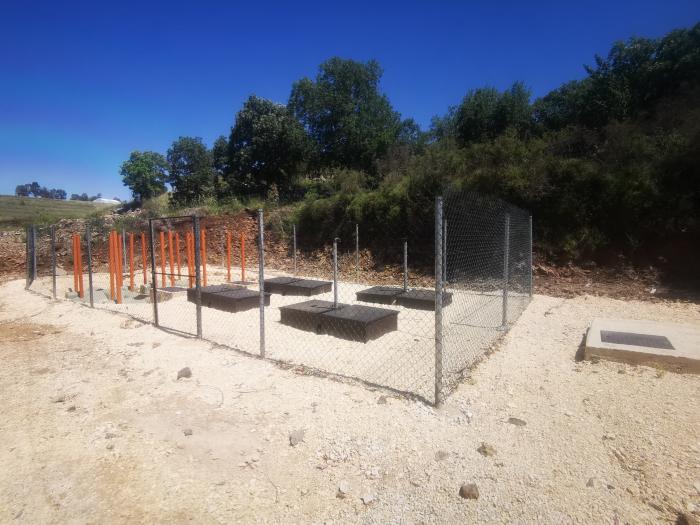
DEWAT chain for the host Community
Description of the emergency context
Menjez is a small village of around 1,000 registered voters, located at an altitude of 350 m above sea level in the Governorate of Akkar, Northern Lebanon, and close to the Syrian border.
Menjez lacks a sewage network, which means that each house disposes of its wastewater in a pit that ultimately flows into a nearby river.
The targeted households did not have a pit and were directly connected to a open sewer which resulted in odors, mosquitos, and other insects downstream, which caused tensions and complaints amongst the village dwellers.
Description of the treatment process
For secondary treatment, the system uses filter media technology (100 m2/m3), comprising of:
- an Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR)
- an Anaerobic Filter (AF);
For tertiary treatment, it relies on Slow Sand Filtration (SSF) and is thus gravity-based.
The system is passive in terms of energy input, and has been in matured operational status since early 2022.
Assessment & design (feasibility)
Solidarités international (SI) carry out consultation sessions first with the Municipality and then, with facilitation from the Municipality, with the dwellers of the pilot group. The Mayor and the dwellers interviewed by the Evaluation Team mentioned that the consultation sessions attempted to probe them for feedback on the designs, but that the respondents did not have the technical know-how for this, which made the sessions more informative than consultative.
From the interviews made, one can confirm that the rate of social acceptance of the intervention is high; it is recognized that the installed DEWATS have effectively solved the problems that were at the origin of the intervention (odors, insects, general pollution hazard).
Construction
These systems are handling relatively low strength influent wastewater streams which do not reflect ITS conditions, but domestic wastewater characteristics. This might explain why the treatment efficiency was almost half that of systems handling ITS waste; if the incoming concentration is lower, and that value is used to calculate removal efficiency, then the removal efficiency would be less. What is important however, is that the effluent produced is similar to those produced by other systems handling stronger wastes with lower hydraulic loads of ITS context (35 L/cap.d), while also treating higher hydraulic loads corresponding to higher wastewater generation rates of Lebanese citizens (150 L/cap.d).
The system tanks being steel type had one of its compartment covers was stolen, and while originally the SSF compartment was kept uncovered by way in keeping in line with the unified design of Batch 3 systems, SI will be installing covers for the SSF compartment in order to eliminate odors currently emanating from it. Still the system can be said to be operational and effective. In fact, the Menjez Municipality will be cashing on this success story to attract funds for a larger-scale intervention.






Add new comment